Fundamental analysis of stock market. Fundamental analysis is a method of evaluating a stock by examining the underlying factors that influence its value. The goal is to determine a stock’s intrinsic value and assess whether it is overvalued or undervalued compared to its current market price.

1. Key Financial Ratio, Fundamental Analysis of Stock Market
A. Valuation Ratio: The valuation ratio is a key concept in fundamental analysis used to assess the relative value of a company. These ratios help investors determine whether a company’s stock is overvalued, undervalued, or fairly priced based on its financial performance, market value, and peer comparisons. Below are some common valuation ratios and their fundamentals:
for example – PE Ratio, PB Ratio, PS Ratio, P/CF Ratio
B. profitable Ratio: Profitability ratios are essential in fundamental analysis to evaluate a company’s ability to generate profits relative to its revenue, assets, equity, or other financial metrics. These ratios are key indicators of financial health and operational efficiency.
for example- operational profit, cross profit, net profit, ROA, ROE, ROCE, EPS.
C. Liquidity Ratio: Liquidity ratios measure a company’s ability to meet that short-term obligations handle with current assets. These ratios are critical in fundamental analysis of stock market to assess financial health and solvency.
for example-Current Ratio, Quick Ratio, Cash Ratio, Working Capital, operation cash flow ratio.
D. Debt Ratio: The debt ratio is a key financial metric used in fundamental analysis of stock market to assess a company’s financial leverage. This ratio helps determine the company’s risk level and long-term solvency.
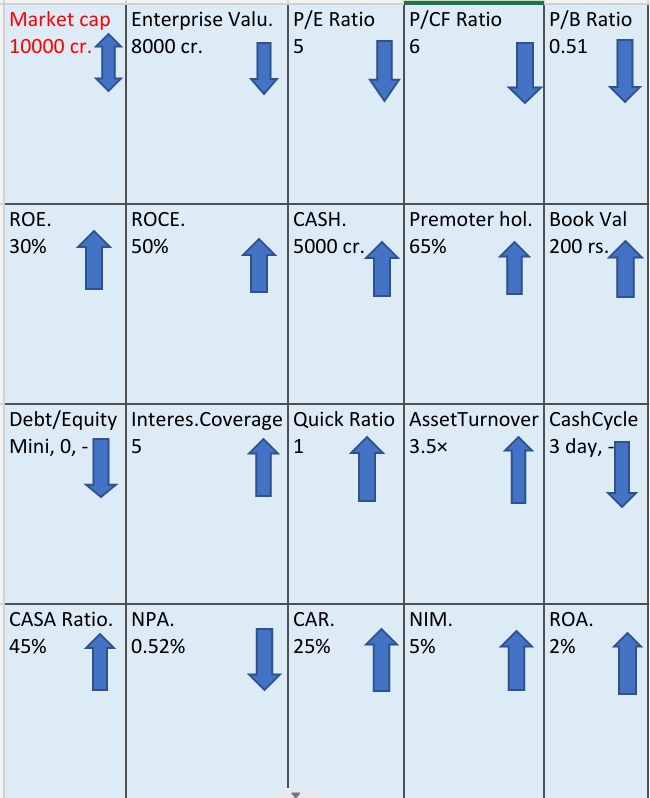
That Chart is very helpful for analysis of stock which basic to fundamental analysis of stock market
This arrow direction indicate that the further in the direction (up or down) of the arrow the stock is undervalued. That means stock is lowest price. this is basic fundamental analysis of stock market.
2. Company Analysis
Company analysts are professionals who evaluate a business’s performance, market position, and potential for growth or investment. Their work typically involves analyzing financial data, market trends, and operational metrics to provide insights that support decision-making. Depending on their role, they may work internally within a company or externally as part of a consulting or financial firm. Fundamental analysis of stock market is critical part of company analysis.
A. Quantitative Analysis
1.Financial Analytics:
Identify potential risks (financial, operational, market-related).
Focus on financial statements, profitability, cash flow, and budgets.
Assess financial performance and make forecasts.
Provide recommendations for investments, mergers, or acquisitions.
2. Market Analysts:
Study market trends, customer behavior, and competitive landscapes.
Offer insights to improve market share and product positioning.
3. Data Analysts:
Process and interpret large datasets to inform strategic decisions.
Use statistical tools and software for pattern recognition.
4. Operations Analysts:
Operational analysis can be improve operation and reduce costs by fundamental analysis of stock market.
Identify bottlenecks and suggest operational improvements.
5. Risk Analysts:
Create unique strategies to mitigate or manage these risk.
B. Management Quality Analysis
Assessing the quality of a company’s management is critical in evaluating its long-term success. Strong management drives strategic decisions, innovation, and organizational efficiency.
1. Leadership Experience: Evaluate the CEO, executive team, and board of directors.
Look at their track records in the industry, including previous successes and failures.
2. Strategic Vision: Assess whether management has a clear, well-communicated vision.
Review their ability to adapt to market changes and disruptions.
3. Operational Efficiency: Analyze how effectively management allocates resources and controls costs.
Look for evidence of process improvements and innovative practices.
4. Corporate Governance: Check for transparency in decision-making and adherence to ethical practices.
Review shareholder relations, including communication and equitable treatment.
5. Employee Engagement: High-quality management fosters a positive company culture and employee satisfaction.
Low turnover rates and strong Glassdoor reviews can indicate effective leadership.
6. Execution of Plans: Evaluate the success rate of strategic initiatives or business expansion efforts.
Look at historical performance against stated objectives.
7. Financial Stewardship: Review how effectively management handles financial resources, including debt, equity, and cash flow.
C. Competitive Analysis
Competitive analysis identifies a company’s position relative to its competitors and helps understand its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
3. Economical Analysis
A. GDP Economic Analysis: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a critical indicator of a country’s economic performance, representing the total monetary value of all goods and services produced within its borders over a specific time. Understanding GDP is fundamental to assessing economic health, identifying growth opportunities, and making informed investment decisions.
B. Interest Rates in Fundamental Analysis: Interest rates are a critical factor in fundamental analysis of stock market as they influence economic growth, corporate profitability, and investment decisions. Analyzing interest rates helps investors understand how monetary policy and economic conditions affect markets, sectors, and individual companies.
C. Global Event: Global events can significantly impact the stock market by influencing investor sentiment, market dynamics, and the fundamentals of economies and industries. These events often trigger volatility, shifts in market trends, and re-evaluation of asset valuations.
D. Government Policy: Government policy and Rule affect stock market. Stock market movement can be heigh and low so fundamental analysis of stock market is compulsory for stock analysis.
4. Advantage of Fundamental Analysis of Stock Market
Fundamental analysis of stock market offers several advantages, especially for investors and analysts aiming to make informed decisions about stocks, bonds, or other financial instruments. Here are the key advantages:
1. Understanding Intrinsic Value: By comparing intrinsic value to the current market price, investors can identify whether an asset is undervalued or overvalued.
2. Long-Term Investment Insights: It focuses on a company’s core financial health, industry position, and growth potential, making it particularly useful for long-term investors. It aids in identifying stable companies with sustainable earnings and growth.
3. Holistic View of the Business: Fundamental analysis involves examining financial statements, management quality, industry trends, and macroeconomic factors, providing a comprehensive understanding of the business.
4. Informed Decision-Making: By understanding the underlying factors that affect an asset’s performance, investors can make more informed and rational decisions rather than relying on market speculation or emotions.
5. Identifying Growth Opportunities: It helps in spotting companies with strong fundamentals and high growth potential, even if they are currently undervalued by the market.
6. Risk Mitigation: Fundamental analysis emphasizes the financial stability and resilience of a company, which can help investors avoid risky or poorly performing investments.
7. Adaptability Across Markets: It can be applied to various types of investments, including equities, fixed income, and even macroeconomic analysis, making it a versatile tool for different asset classes.
8. Focus on Long-Term Trends: Unlike technical analysis, which focuses on short-term price movements, fundamental analysis emphasizes long-term trends and sustainability, aligning well with investment strategies aimed at wealth accumulation.
9. Supports Value Investing: This method is the cornerstone of value investing, as practiced by investors like Warren Buffett, who seek to buy high-quality companies at a discount to their intrinsic value.
10. Objective Framework: By relying on data and financial metrics, fundamental analysis of stock market reduces subjectivity and provides a more objective approach to evaluating investment opportunity.
5. Disadvantage of Fundamental Analysis of Stock Market
While fundamental analysis of stock market has numerous advantages, it also comes with certain disadvantages and limitations. Here are the key drawbacks:
1. Time-Consuming: Fundamental analysis of stock market requires extensive research and evaluation of financial statements, industry trends, and economic factors, making it a labor-intensive process.
2. Complexity: Analyzing a company’s fundamentals involves interpreting financial ratios, understanding industry dynamics, and assessing macroeconomic influences, which can be complex and challenging for beginners.
3. Subjectivity: Some aspects of fundamental analysis of stock market, such as evaluating management quality or future growth potential, involve subjective judgment, which can lead to biases.
4. Limited Applicability for Short-Term Trading: Fundamental analysis of stock market focuses on long-term value, making it less useful for short-term traders who rely more on technical analysis or market sentiment.
5. Sensitivity to Assumptions: The outcomes of fundamental analysis are heavily dependent on the assumptions used in valuation models, such as growth rates, discount rates, and future earnings.
6. Market Inefficiencies: Even if an asset is undervalued or overvalued based on fundamental analysis, it may take a long time for the market to recognize this, during which the investor could face volatility.
